Methods
A method is an action that an object can perform. So far, you have used methods but not created them yourself. Now it's time to create methods.
Unlike constructors, methods must include a return type. A return type is the kind of information a method sends back to the caller of the method. You can think of this like a function in mathematics. If we define function f(x) = 2*x then calling f(5) returns 10. 10 is the returned value and its return type is an integer.
In Java, function f(x) would be written as a method with an int return type:

To call this method outside its class you would write something like bob.f(5); where bob is an object of the class type that f(x) is defined in. We will discuss how to use methods with return values in Lesson 4.
Methods that do not return a value have a return type of void. This is the kind of method you need for your house project.
Let's add a draw() method to our Window class:
public class Window {
// Attributes
...same as before
// Constructors
...same as before
// Methods
public void draw() {
pen.up(); // Move to window location
pen.move(-200, 0);
pen.setDirection(90);
pen.down();
pen.drawRect(100, 100); // Draw the window
pen.forward(50);
pen.backward(100);
pen.forward(50);
pen.turnRight(90);
pen.forward(50);
pen.backward(100);
}
}
There are two problems with the code above.
- There is no pen object defined so nothing can be drawn
- The drawing is hard-coded, meaning that its position, size, and colors are fixed rather than dependent upon the attribute values.
To solve the issue of not having a pen object, we could try to create a new SketchPad and DrawingTool:
public void draw() {
Sketchpad pad = new SketchPad(800, 600):
DrawingTool pen = new DrawingTool(pad);
pen.up(); // Move to window location
pen.move(-200, 0);
pen.setDirection(90);
pen.down();
pen.drawRect(100, 100); // Draw the window
pen.forward(50);
pen.backward(100);
pen.forward(50);
pen.turnRight(90);
pen.forward(50);
pen.backward(100);
}
Unfortunately, this won't work because every time we call the draw() function, the window object will be drawn in a new SketchPad.
Instead of this:
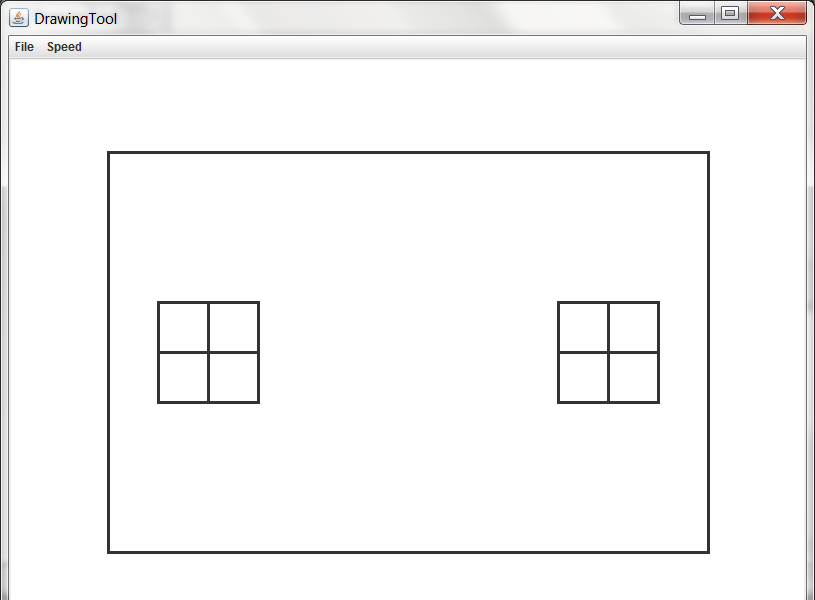
We'll get this:
A correct approach would be to add a DrawingTool attribute to the Window class and allow the user of our Window class to specify which SketchPad to draw in through the constructor:
public class Window {
// Attributes
.. same as before DrawingTool pencil;
// Constructors
public Window(int x, int y, SketchPad pad) {
// Use the constructor parameters x and y to initialize the xPos and yPos attributes
xPos = x;
yPos = y;
// Use the constructor parameter pad to initialize the pencil to DrawingTool that draws in that pad
pencil = new DrawingTool(pad);
...same as before
...
}
Now we have a working Window class.
public class Window {
// Attributes
int xPos;
int yPos;
int width;
int height;
Color frameColor;
Color interiorColor;
DrawingTool pencil;
// Constructors
public Window(int x, int y, SketchPad pad) {
// Use the constructor parameters to initialize the xPos, yPos, and pencil attributes
xPos = x;
yPos = y;
pencil = new DrawingTool(pad);
// Choose default values for the rest of the attributes
width = 100;
height = 100;
frameColor = Color.BLACK;
interiorColor = new Color(255, 255, 0);
}
// Methods
public void draw() {
pencil.up(); // Move to window location
pencil.move(-200, 0);
pencil.setDirection(90);
pencil.down();
pencil.drawRect(100, 100); // Draw the window
pencil.forward(50);
pencil.backward(100);
pencil.forward(50);
pencil.turnRight(90);
pencil.forward(50);
pencil.backward(100);
}
}
Because we have hard-coded the window values, Window objects will always be centered at (-200, 0) with a width and height of 100. Let's replace the hard-coded values with our attributes so that Window objects are based on the attribute values.
public class Window {
// Attributes
int xPos;
int yPos;
int width;
int height;
Color frameColor;
Color interiorColor;
DrawingTool pencil;
// Constructors
public Window(int x, int y, SketchPad pad) {
// Use the constructor parameters to initialize the xPos, yPos, and pencil attributes
xPos = x;
yPos = y;
pencil = new DrawingTool(pad);
// Choose default values for the rest of the attributes
width = 100;
height = 100;
frameColor = Color.BLACK;
interiorColor = new Color(255, 255, 0);
}
// Methods
public void draw() {
pencil.up(); // Move to window location
pencil.move(xPos, yPos);
pencil.setDirection(90);
pencil.down();
pencil.setColor(interiorColor); // Change color before drawing interior of window
pencil.fillRect(width, height); // Draw interior of window
pencil.setColor(frameColor); // Change color before drawing outer frame of window
pencil.drawRect(width, height); // Draw the window
pencil.forward(height/2);
pencil.backward(height);
pencil.forward(height/2);
pencil.turnRight(90);
pencil.forward(width/2);
pencil.backward(width);
}
}